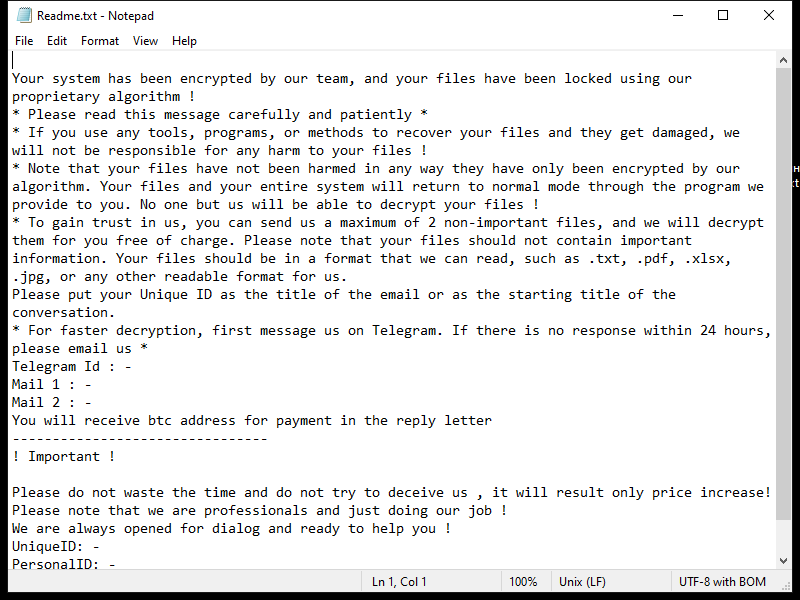
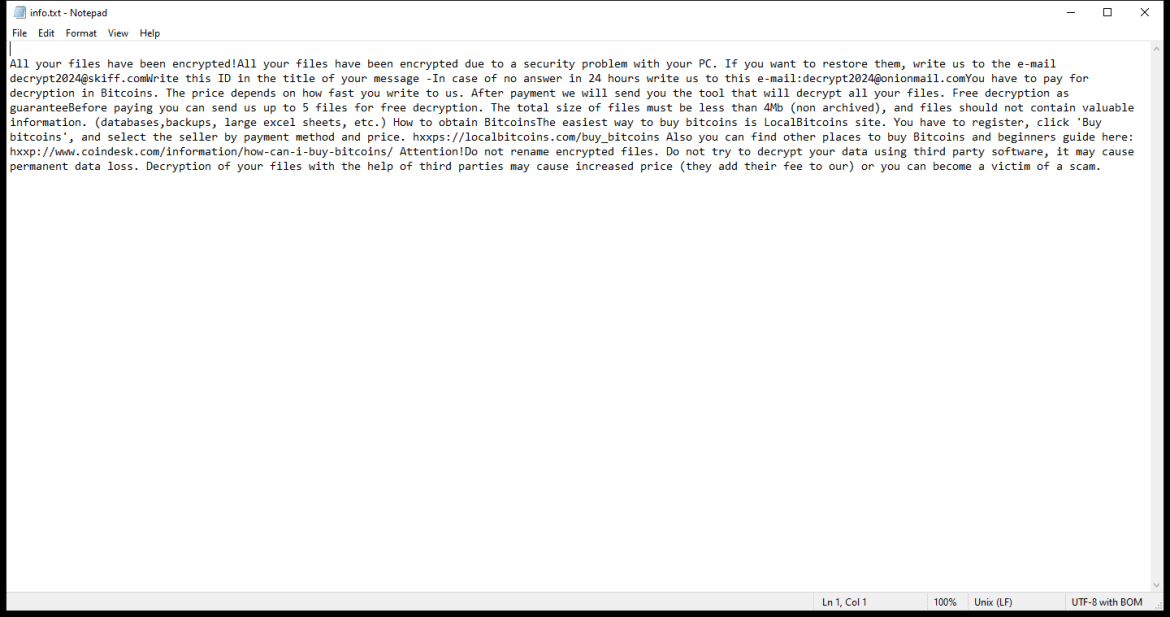
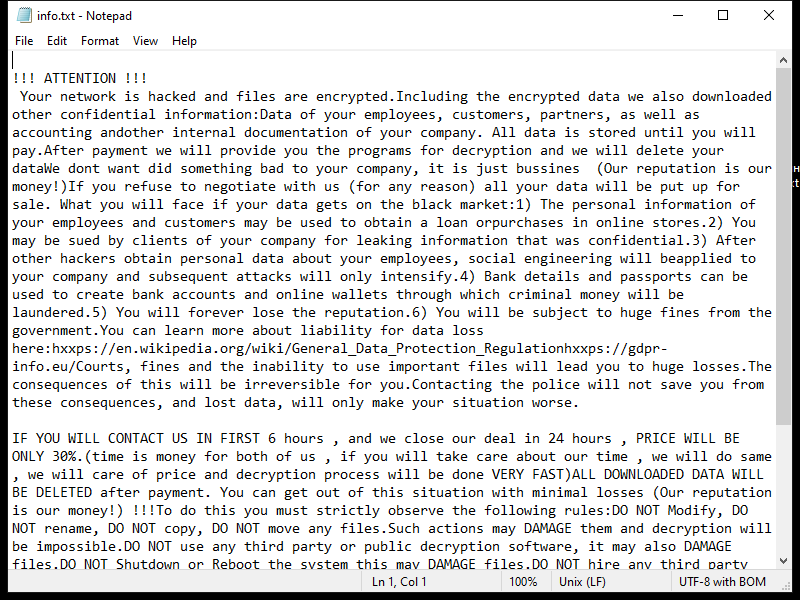
Joker RAT is a dangerous piece of malware that specifically targets Android devices. RAT stands for Remote Access Trojan, which means that once Joker RAT infects a device, it allows remote access and control to cybercriminals. This particular malware variant has gained notoriety due to its ability to silently perform malicious actions and steal sensitive information from infected devices.
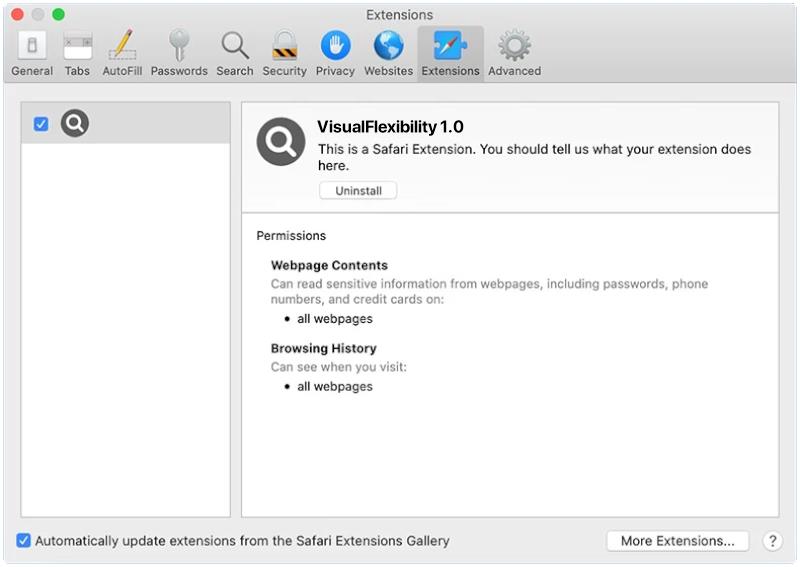
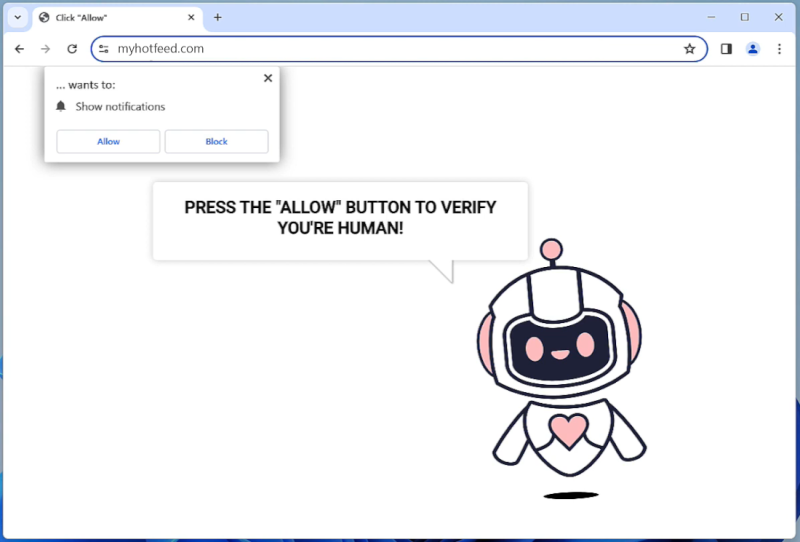
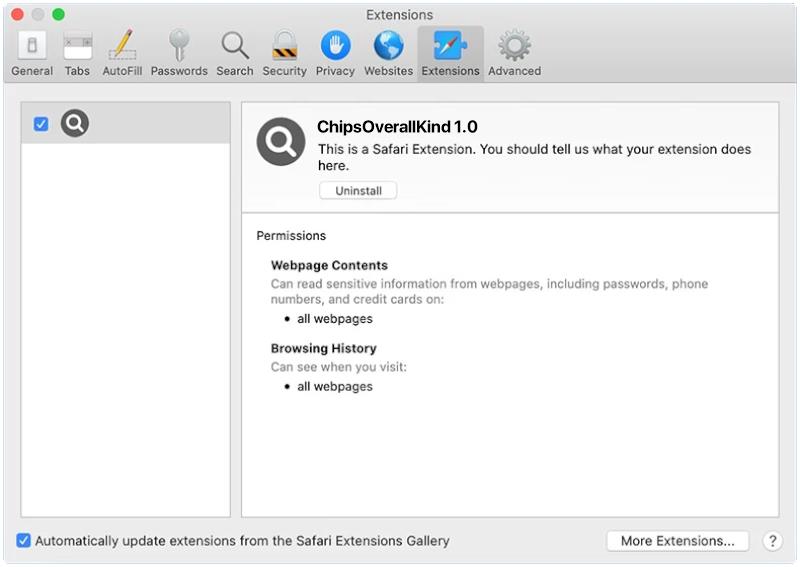
Joker RAT primarily infects Android devices through malicious apps available on third-party app stores and websites. It often disguises itself as a legitimate application, such as a gaming or utility app, to trick users into downloading and installing it. Once the app is installed, Joker RAT starts its malicious activities by secretly subscribing the victim to premium services without their consent. These services often come with a recurring fee that is charged to the victim’s mobile account. Additionally, the malware can also steal SMS messages, contact lists, and other personal data, which can be further exploited by cybercriminals for various illegal activities.
It is crucial for Android users to be cautious while downloading apps from outside the official Google Play Store, as this is the primary source for Joker RAT infections. Users should only download apps from trusted sources and carefully review app permissions before installation. Additionally, keeping devices updated with the latest security patches and using reliable antivirus software can help in detecting and preventing Joker RAT infections. Stay vigilant and prioritize cybersecurity to protect your Android device from the ever-evolving threats posed by malware like Joker RAT.