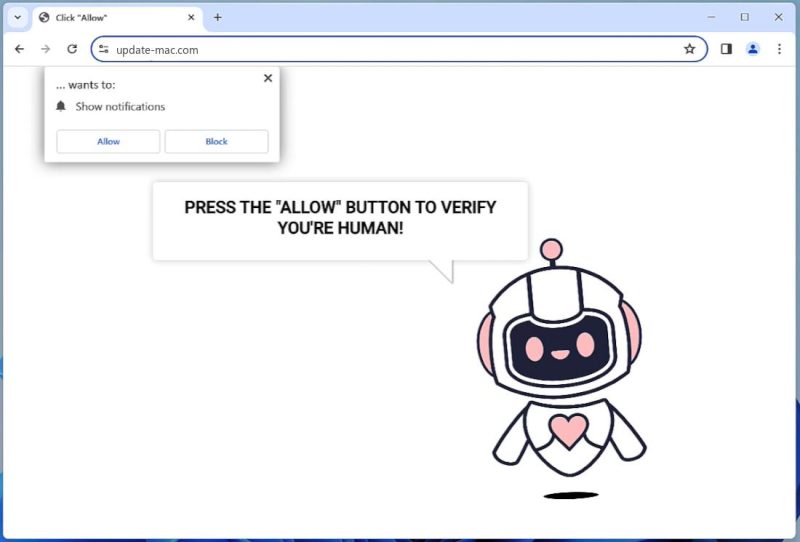
Ssj4.io is a type of adware that infects computers and browsers by displaying intrusive and unwanted advertisements to users. It typically infiltrates systems through deceptive methods, such as bundling with free software or disguising itself as a legitimate program or browser extension. Once installed, Ssj4.io starts to modify the browser settings and redirect users to its own domain, where various ads are presented.
The adware gains control over the browser by altering its settings, including the default search engine, homepage, and new tab page. As a result, whenever users open their browser or perform a search, they are redirected to Ssj4.io or other affiliated advertising websites. These ads can be in the form of pop-ups, banners, in-text links, or even full-page advertisements. Ssj4.io aims to generate revenue through pay-per-click schemes, as each click on the ads provides income to the developers. Additionally, the adware may collect users’ browsing data, such as their search queries, visited websites, and IP addresses, to further tailor the advertisements displayed and potentially sell the information to third parties.