Shiel Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files on a victim’s computer and demands a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. Here are the details about Shiel Ransomware without any links or references:
1. Infection Method: Shiel Ransomware typically infects computers through various means, such as malicious email attachments, fake software updates, infected websites, or exploiting vulnerabilities in software.
2. File Extensions: Shiel Ransomware adds a specific extension to the encrypted files, which can vary with different versions of the ransomware. However, it commonly uses extensions like “.shiel” or “.shield” appended to the original file extension.
3. File Encryption: Shiel Ransomware employs strong encryption algorithms like AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) or RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) to encrypt the victim’s files. These encryption algorithms are designed to make decryption without the proper key extremely difficult.
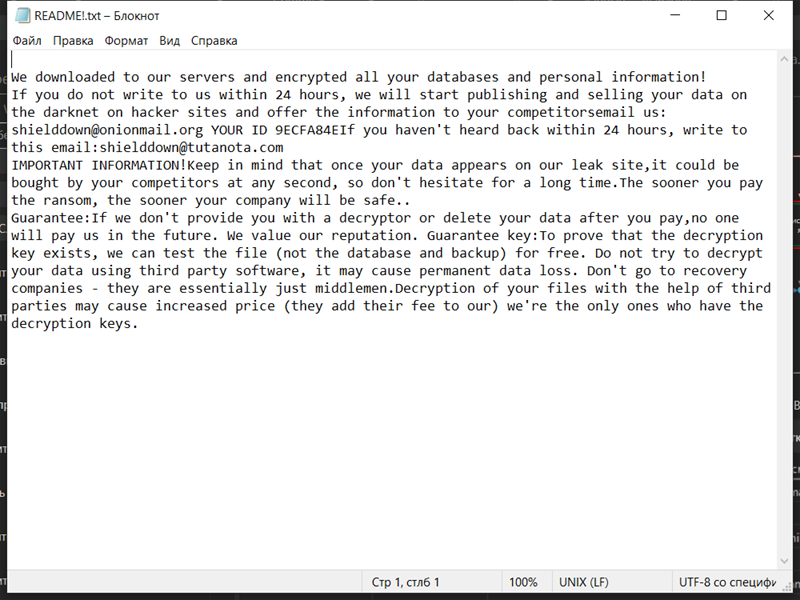
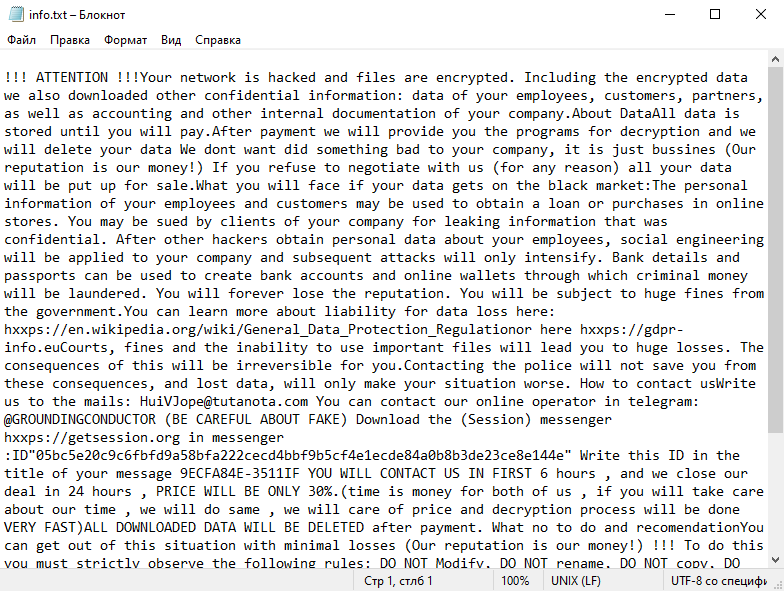
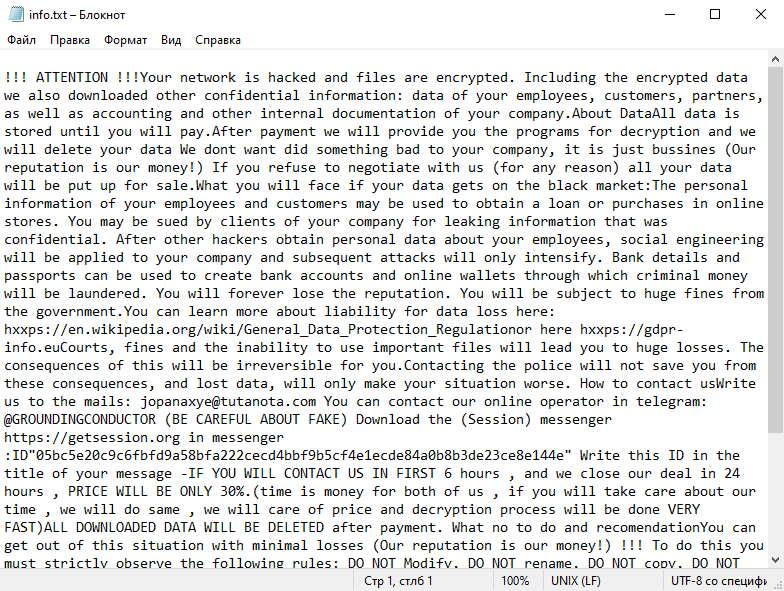
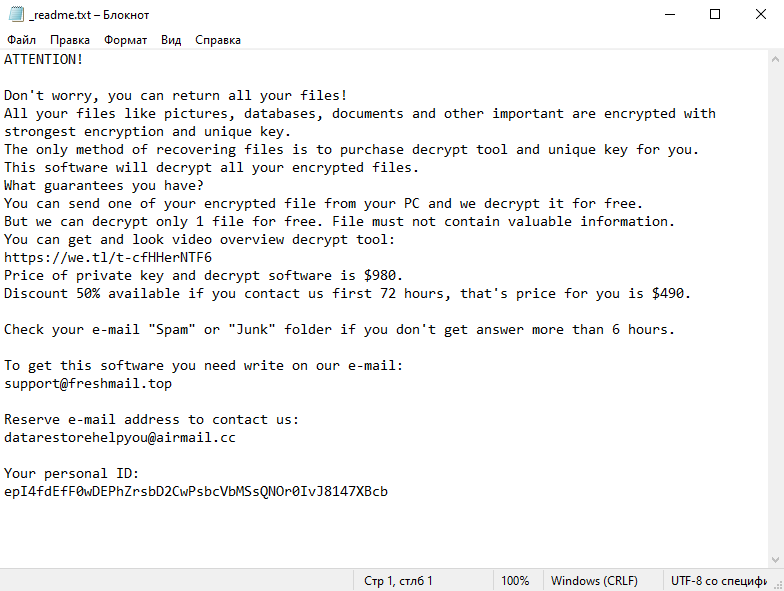
4. Ransom Note: After encrypting the files, Shiel Ransomware creates a ransom note that provides instructions on how to pay the ransom and obtain the decryption key. The ransom note is usually in the form of a text file or a pop-up message on the victim’s screen.
5. Decryption Tools: As of now, there are no known decryption tools available for Shiel Ransomware. It is always recommended to refrain from paying the ransom, as it encourages cybercriminals and may not guarantee the recovery of your files.
6. Decrypting Shiel Files: If you have been a victim of Shiel Ransomware, the best course of action is to restore your files from a secure backup. Regularly backing up your important files on an external device or cloud storage is crucial to mitigate the impact of ransomware attacks. Additionally, you can seek assistance from cybersecurity professionals who may have alternative solutions or techniques to recover your files.
Remember, prevention is better than cure when it comes to ransomware. Maintain updated antivirus software, exercise caution while opening email attachments or visiting unfamiliar websites, and keep your operating system and applications up to date to minimize the risk of infection.