Lkhy Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files on a victim’s computer, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Here are the details you requested:
1. Infection: Lkhy Ransomware typically infects computers through various methods, including malicious email attachments, software vulnerabilities, or by exploiting weak security protocols.
2. File Extensions: Lkhy Ransomware adds the “.lkhy” extension to the encrypted files. For example, a file named “document.docx” would become “document.docx.lkhy” after encryption.
3. File Encryption: Lkhy Ransomware employs a strong encryption algorithm (usually AES) to encrypt the files on the infected computer. This encryption renders the files unreadable without the decryption key.
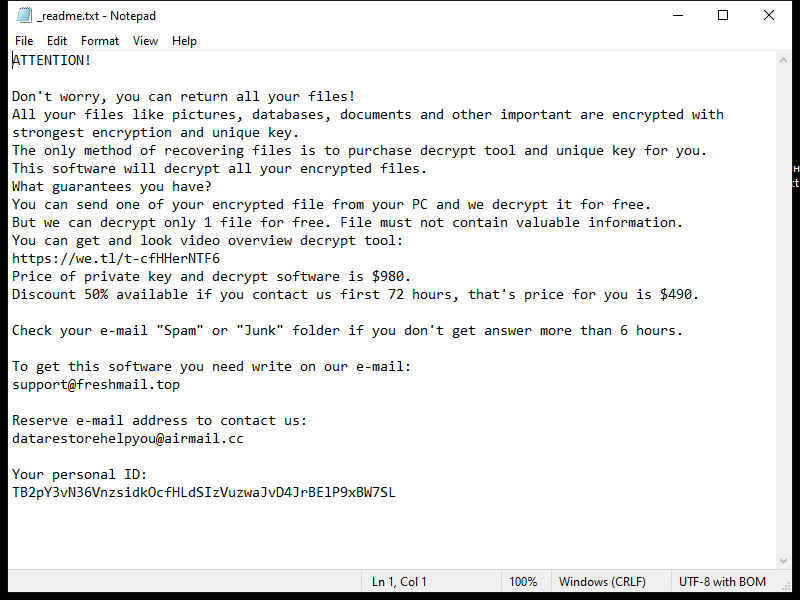
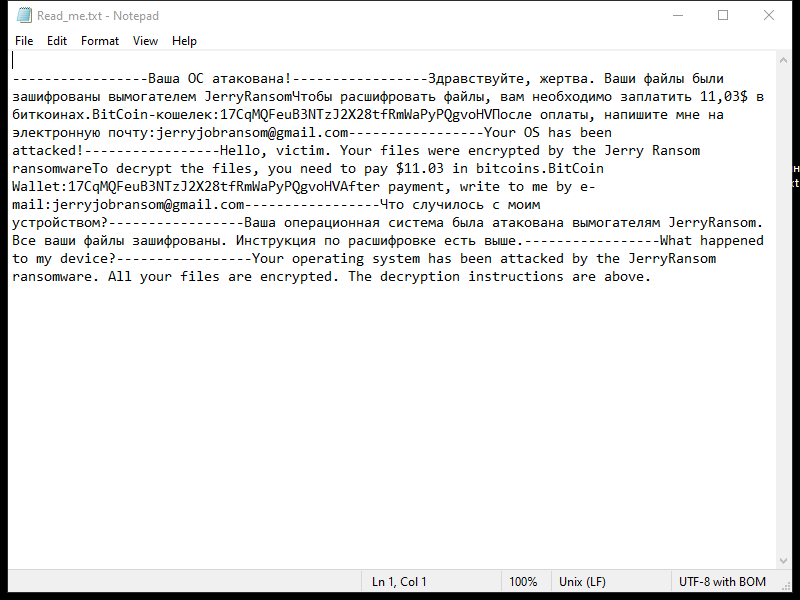
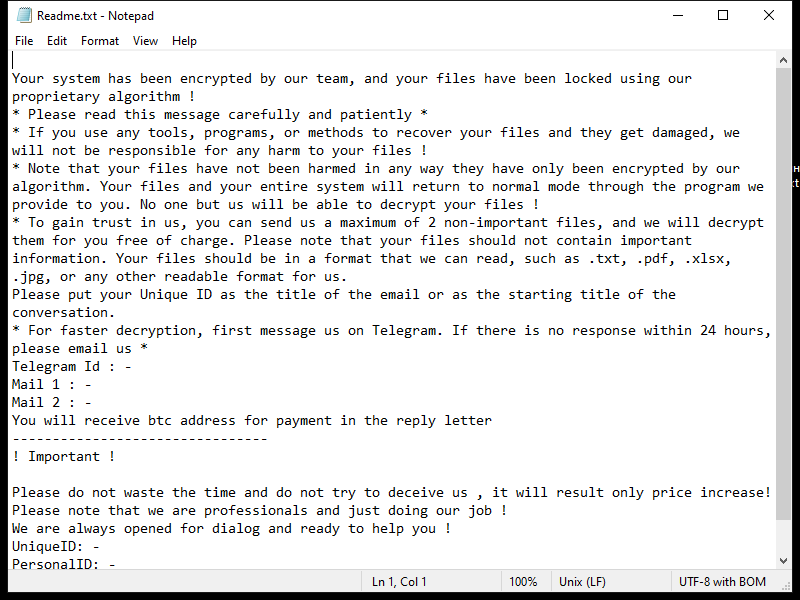
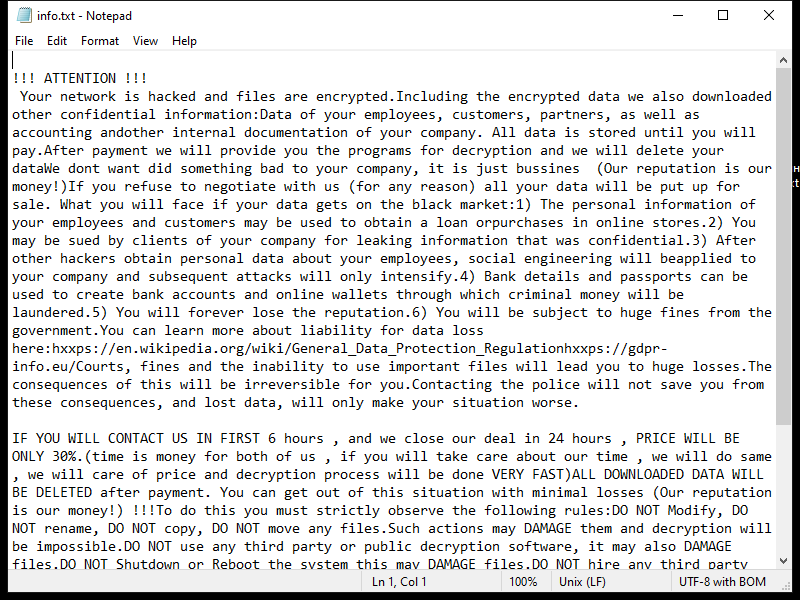
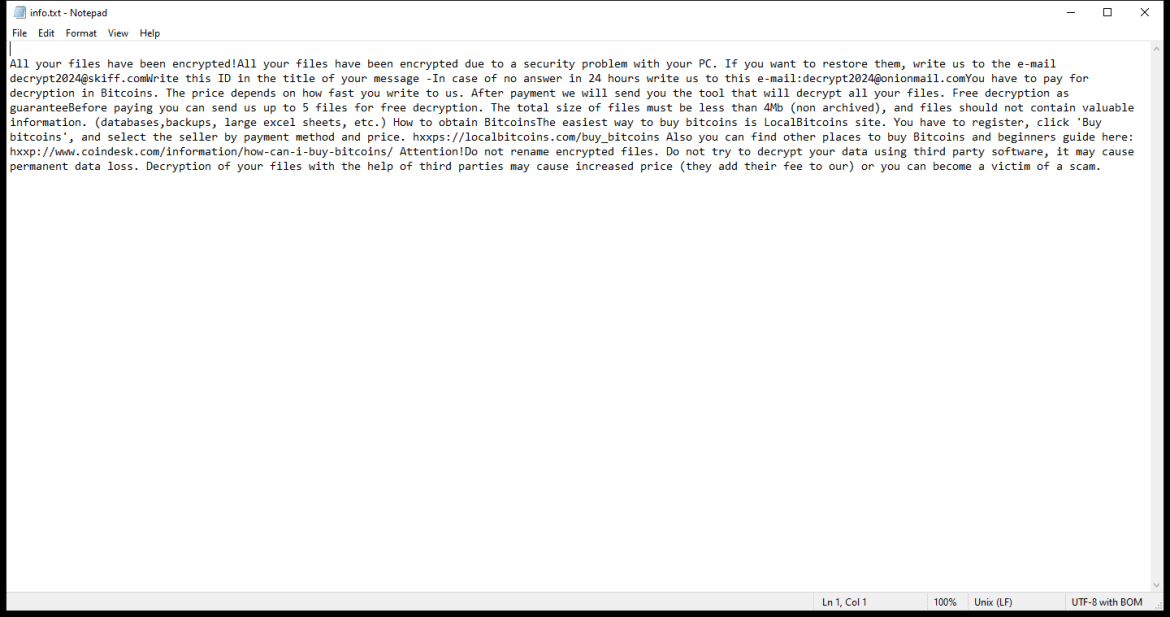
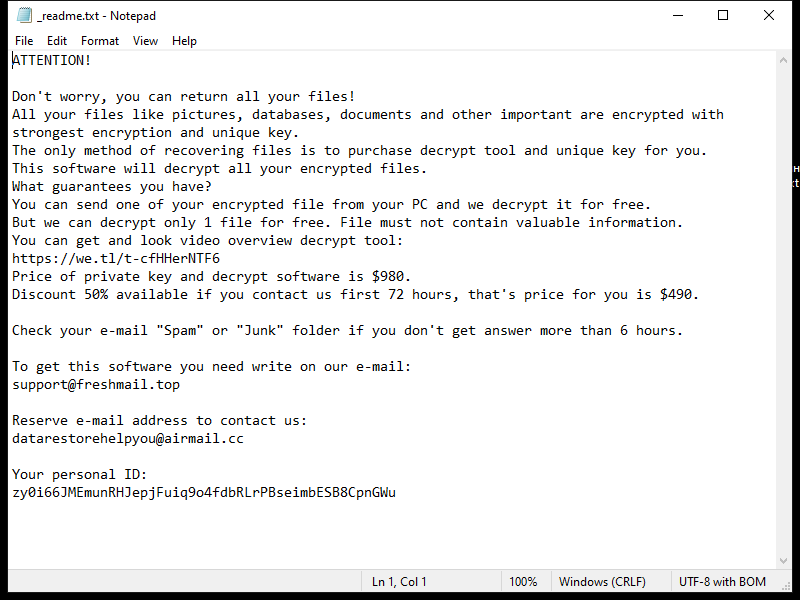
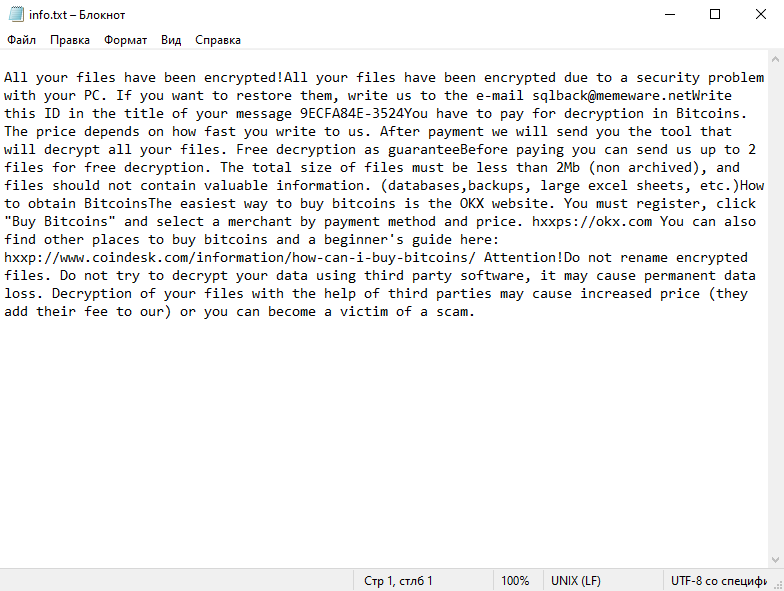
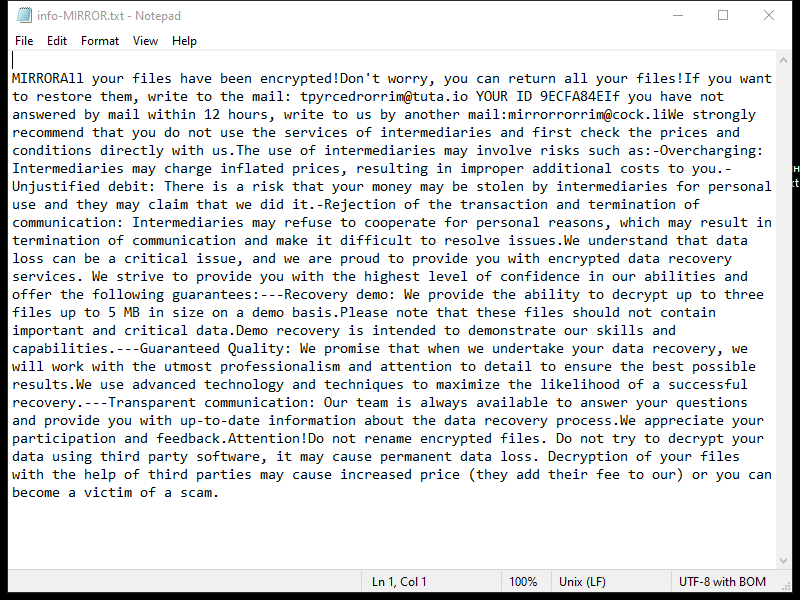
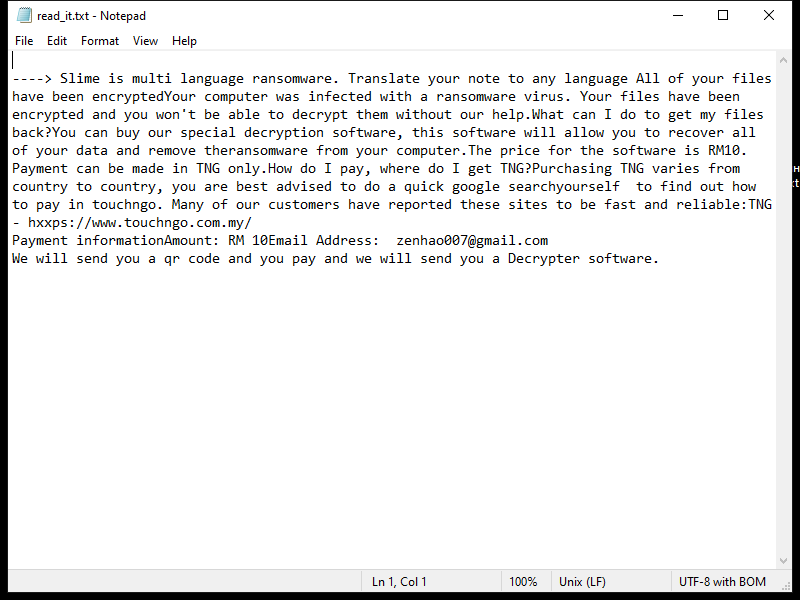
4. Ransom Note: Lkhy Ransomware usually creates a ransom note, commonly named “Readme.txt” or “Readme.html,” which informs the victim about the encryption and provides instructions on how to pay the ransom. The note may also contain threats or warnings to pressure the victim into paying.
5. Decryption Tools: As of now, there is no decryption tool available specifically for Lkhy Ransomware. However, security companies like Emsisoft continue to develop tools to decrypt files affected by different strains of ransomware. You can check their official website or contact their support team to see if a decryption tool is available for Lkhy Ransomware.
6. Decrypting .lkhy Files: Without a decryption tool, it is challenging to decrypt .lkhy files. However, there are a few possible options to consider:
– Restore from Backup: If you have a recent backup of your files, you can restore them after removing the ransomware from your system.
– Contact Security Experts: Reach out to professional cybersecurity firms or local law enforcement agencies who may be able to provide assistance or guidance.
– Wait for Decryption Tool: Keep an eye on security websites or forums for updates on potential decryption tools or solutions.
Remember, it is always recommended to maintain regular backups of your important files and ensure your system has updated security software to minimize the risk of ransomware infections.