CookiesHelper Ransomware is a type of malicious software designed by cybercriminals to encrypt data on a victim’s computer or network, making it inaccessible until a ransom is paid. Once infiltrated, it encrypts various files and data, rendering them unreadable.
Infection Methods:
Ransomware like CookiesHelper typically infects computers through various methods such as phishing scams, malicious email attachments, fake software updates, or by exploiting vulnerabilities in an operating system, software, or network.
File Extensions:
The specific file extensions added by CookiesHelper ransomware can vary, but usually it’s .cookieshelper. However, most ransomware typically adds unique extensions to the encrypted files, often containing the attacker’s contact information or specific identifiers related to the ransomware.
File Encryption:
The exact encryption algorithm used by CookiesHelper ransomware is not specified in the public domain. However, many types of ransomware use advanced encryption algorithms, like RSA or AES, to encrypt the files.
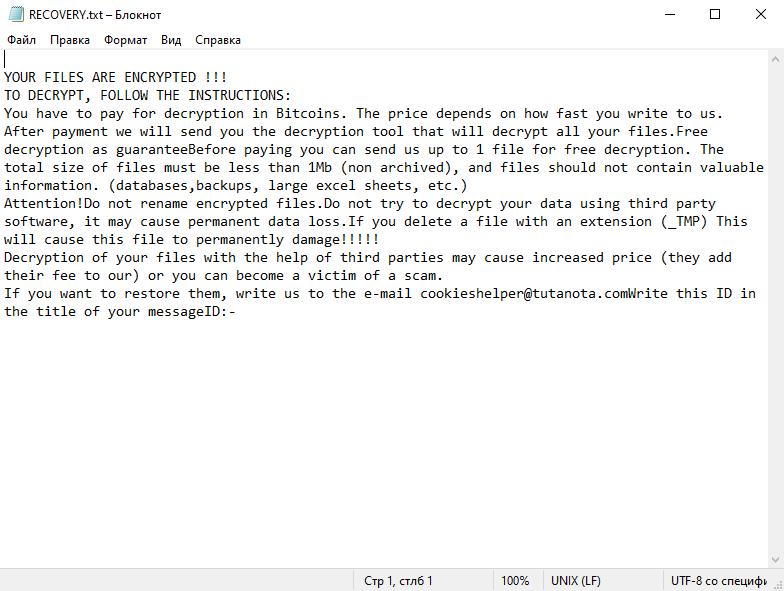
Ransom Note:
After encrypting the files, ransomware typically creates a ransom note explaining what has happened and how to pay the ransom to get the files back. The specific content and location of this note can vary greatly, and the specifics for CookiesHelper ransomware are not publicly available.
Decryption Tools:
Whether a decryption tool exists for CookiesHelper ransomware is also not specifically known. In many cases, unless a security flaw is found in the ransomware or the cybercriminals are apprehended and the decryption keys are released, no reliable decryption tool would be available.
Decrypt .cookieshelper files:
Decrypting files encrypted by ransomware can be complex and is often not possible without the specific decryption key. If a decryption tool is available, it would typically need to be run on the affected computer. The tool would then attempt to decrypt the files. However, due to the potential for data loss, it is generally recommended to back up the encrypted files before attempting decryption.
It’s important to note that paying the ransom is not recommended because it does not guarantee that the files will be decrypted or that the ransomware will be removed from the computer. Instead, victims should remove the ransomware from their system using a reliable anti-malware program and restore their files from a backup if possible.
Read more