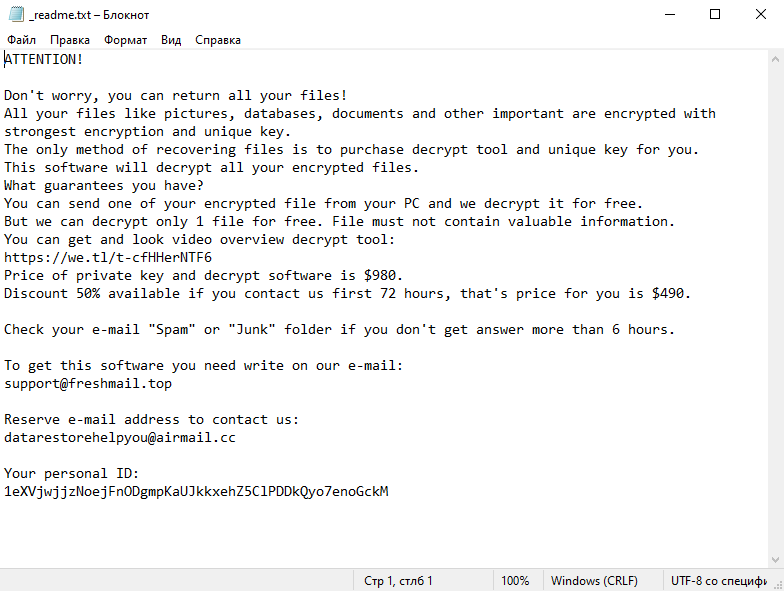
Ljuy Ransomware is a type of malicious software that encrypts files on a victim’s computer and demands a ransom for their decryption. Here is some information about the ransomware:
Infection: Ljuy Ransomware can infect computers through various methods, such as malicious email attachments, software vulnerabilities, fake software updates, or by being bundled with other software.
File Extensions: Ljuy Ransomware typically adds a unique extension to each encrypted file. The specific extension may vary, but it often consists of a combination of random characters.
File Encryption: Ljuy Ransomware uses a strong encryption algorithm to encrypt the victim’s files, making them inaccessible without a decryption key. The encryption algorithm may vary depending on the variant of the ransomware.
Ransom Note: Ljuy Ransomware creates a ransom note that usually appears as a text file or an image file. It is often placed in every folder containing encrypted files or displayed on the desktop. The note typically contains instructions on how to pay the ransom and obtain the decryption key.
Decryption Tools: Emsisoft, a cybersecurity company, has developed a tool called “STOP Djvu Decryptor” that can decrypt files encrypted by various variants of Djvu Ransomware, including some variants of Ljuy Ransomware. However, not all variants are decryptable, and it may not work for all cases.
Decrypting Files: If you have been affected by Ljuy Ransomware and your files have been encrypted, you can try using the Emsisoft STOP Djvu Decryptor tool to decrypt your files. However, it is essential to note that this tool may not work for all variants, and it is always recommended to have a backup of your important files to avoid data loss.
Please note that without specific details about the variant of Ljuy Ransomware and its encryption algorithm, it is challenging to provide precise information. It is always recommended to consult with a cybersecurity professional for assistance in dealing with ransomware attacks.