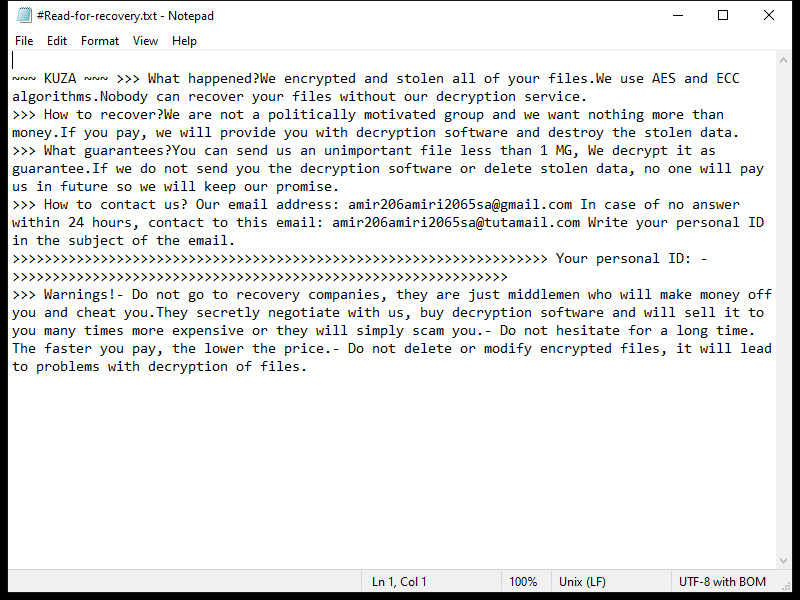
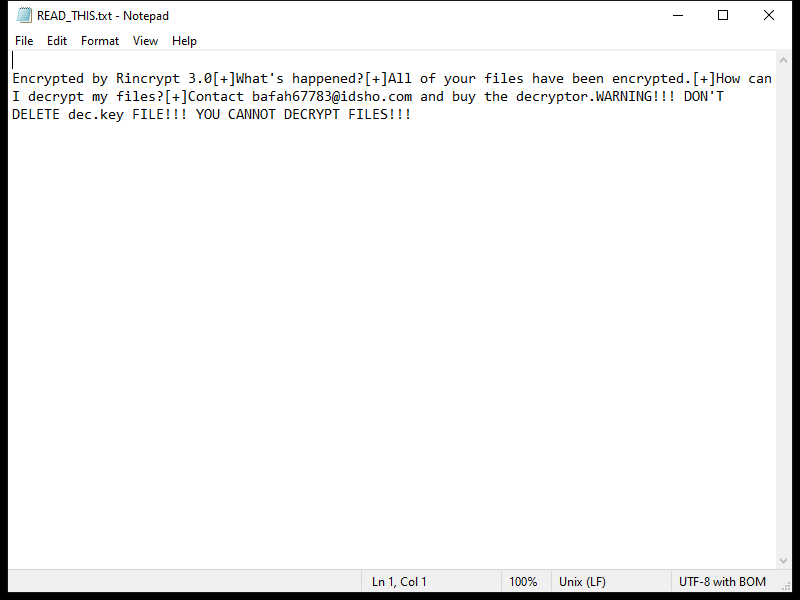
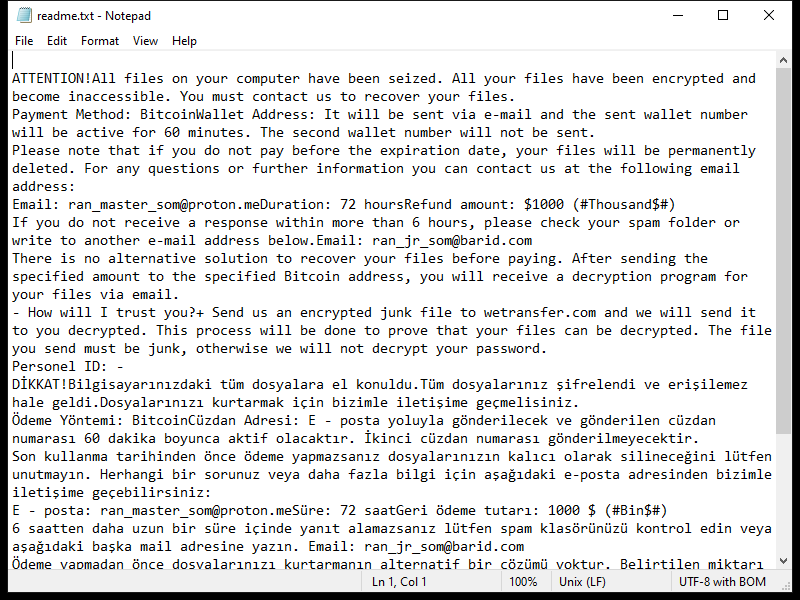
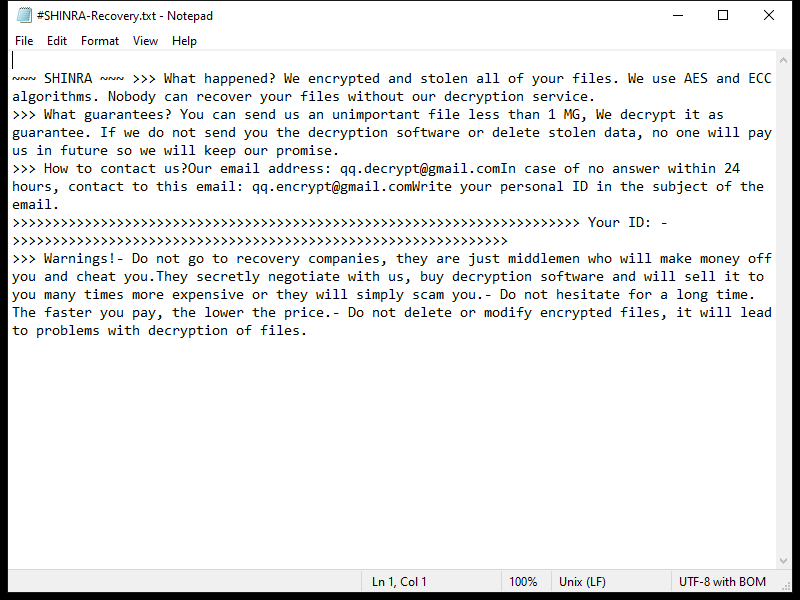
KUZA Ransomware is a type of malicious software that infects computers by encrypting files on the system and demanding a ransom payment in exchange for the decryption key. It typically spreads through phishing emails, malicious websites, or software vulnerabilities.
Once infected, KUZA Ransomware adds a “.ripa” extension to encrypted files, making them inaccessible to the user. The ransomware uses strong encryption algorithms such as AES or RSA to lock the files, rendering them unreadable without the decryption key.
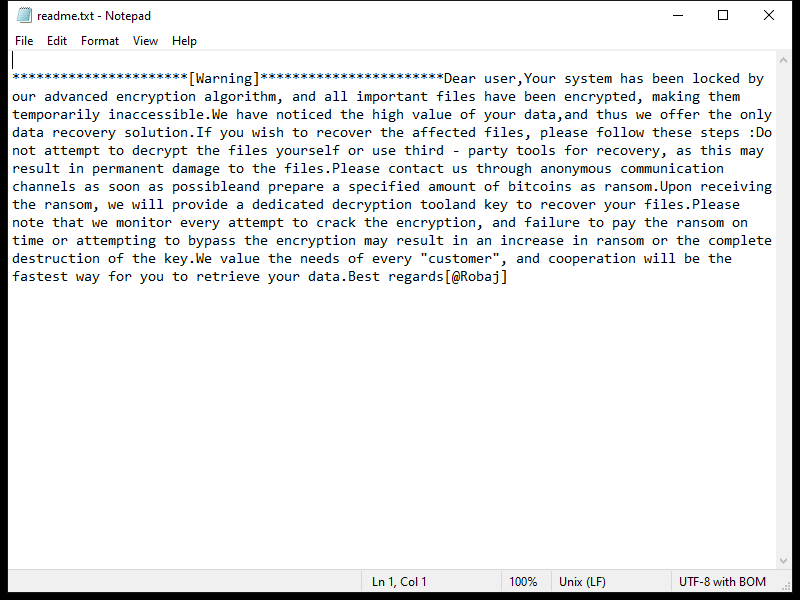
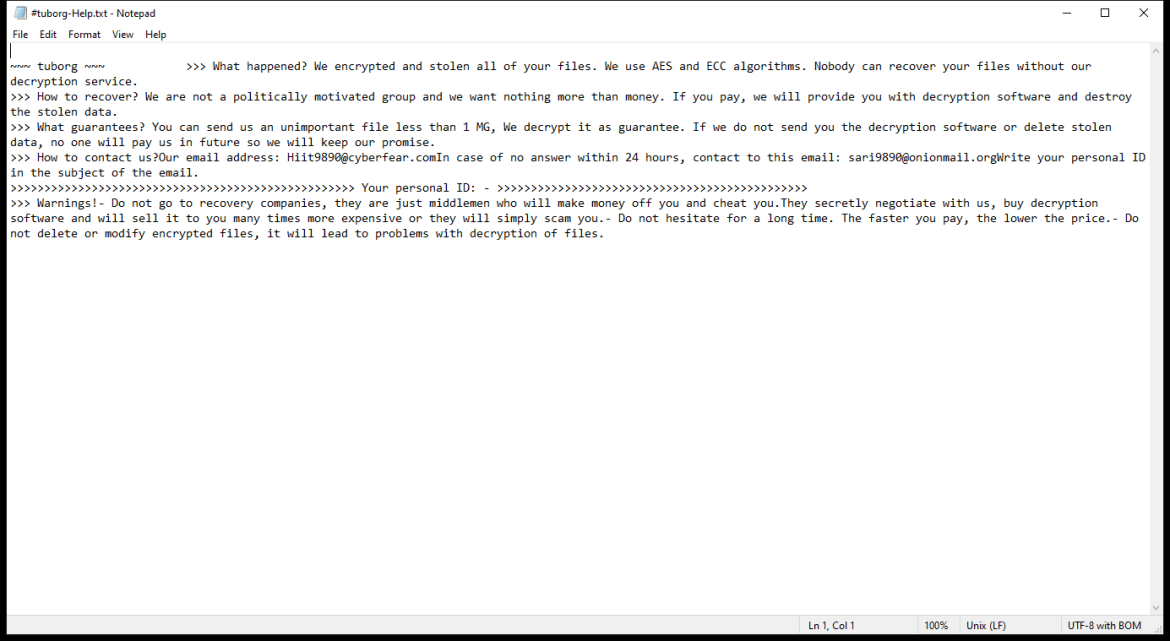
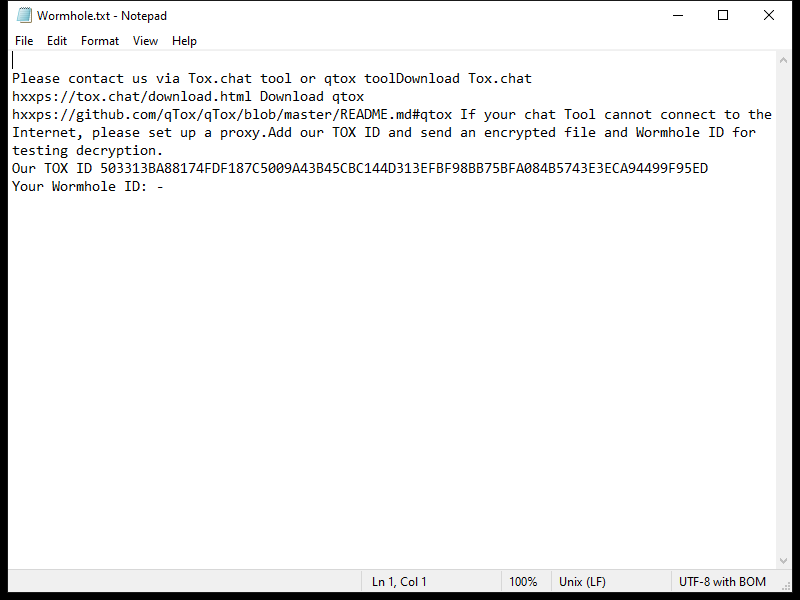
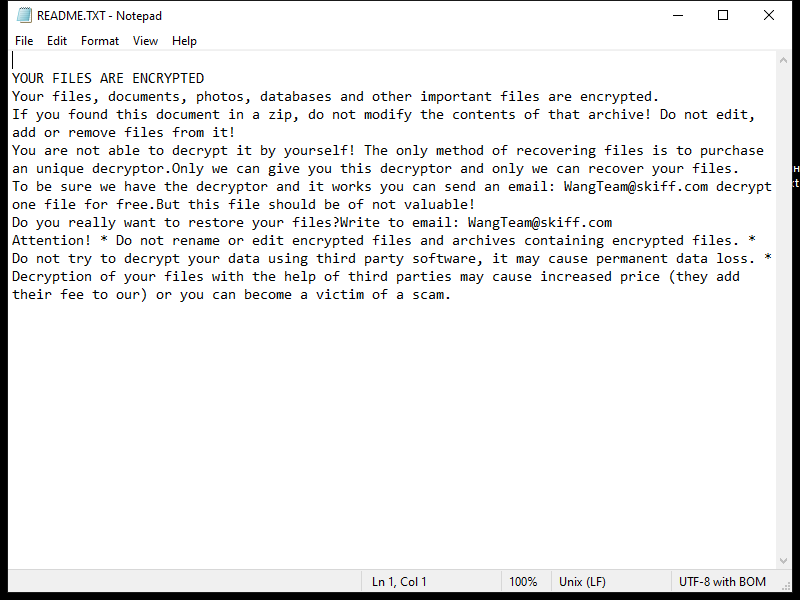
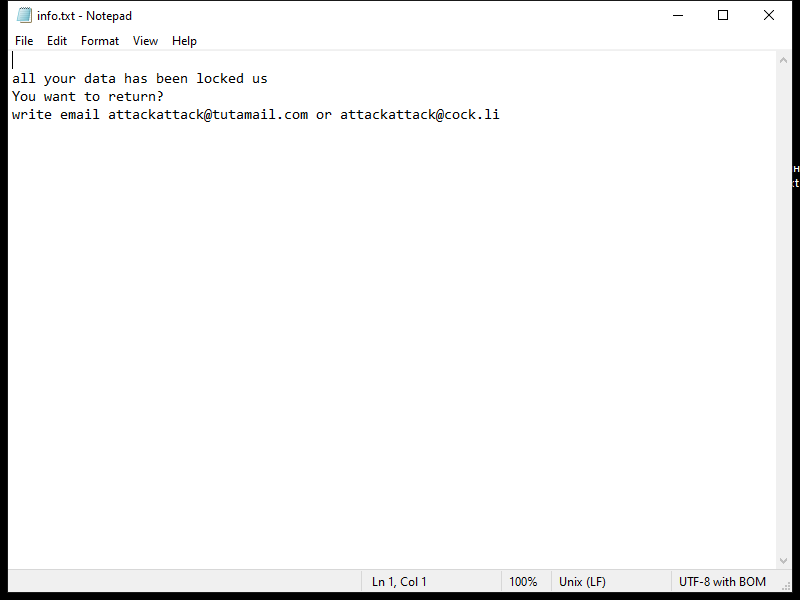
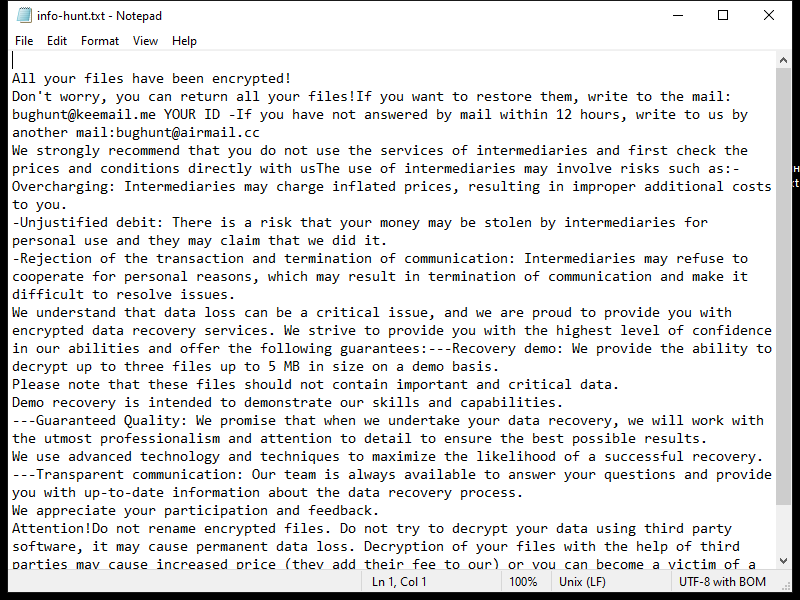
After encrypting the files, KUZA Ransomware creates a ransom note on the desktop or in the affected folders, instructing the victim on how to pay the ransom to receive the decryption key. The note usually contains information on the ransom amount, payment instructions, and contact details for the cybercriminals.
As of now, there are no known decryption tools available for .ripa files encrypted by KUZA Ransomware. However, it is not recommended to pay the ransom as it does not guarantee the safe recovery of your files and may further support criminal activities. Instead, you can try restoring your files from backup, using file recovery software, or seeking help from cybersecurity experts.