Cdmx Ransomware is a type of malicious software that is part of the Djvu/STOP Ransomware family. It’s designed to infiltrate computer systems and encrypt users’ files, making them inaccessible until a ransom is paid.
Infection Method:
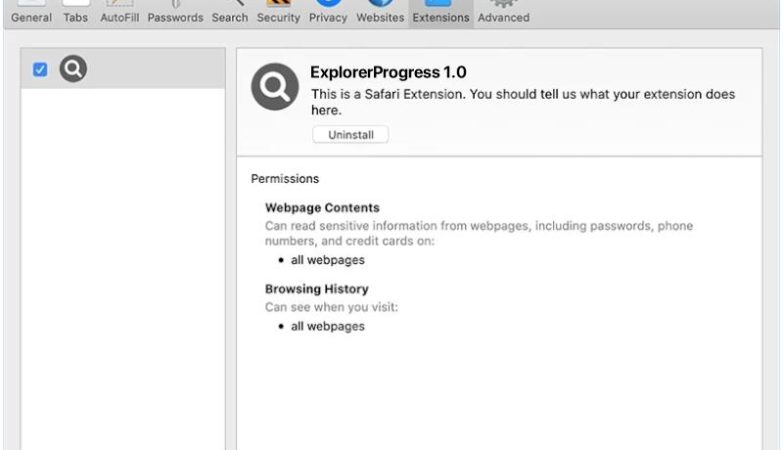
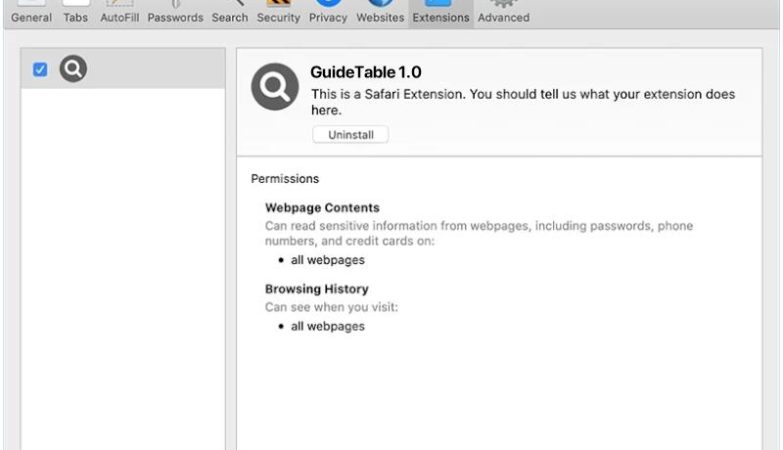
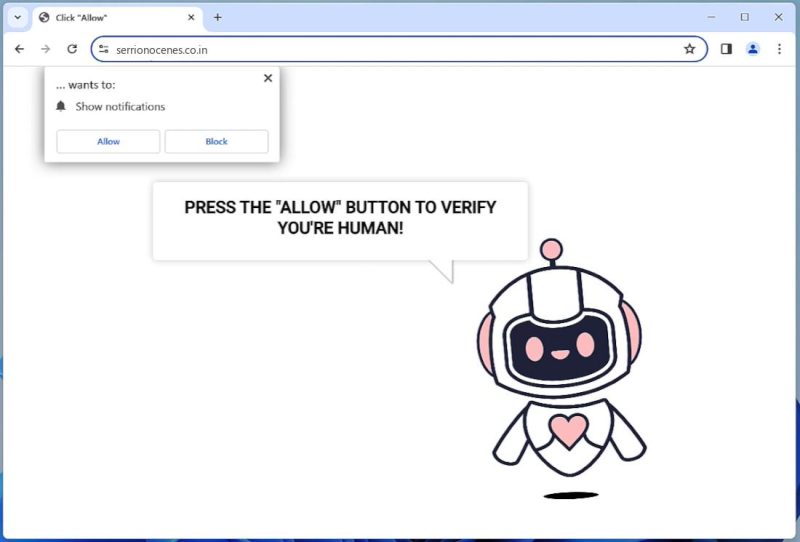
Cdmx Ransomware often infects computers via spam emails, malicious advertisements, or compromised websites. It can also infiltrate a system through unpatched software vulnerabilities or weak passwords.
File Extensions and Encryption:
Once installed, the ransomware scans and encrypts a wide range of file types, such as documents, images, videos, music, etc. It typically appends a unique extension, .cdmx, to the end of each encrypted file’s name, indicating that the file has been encrypted. The encryption method used by Cdmx Ransomware is typically AES-256, a robust and secure encryption algorithm.
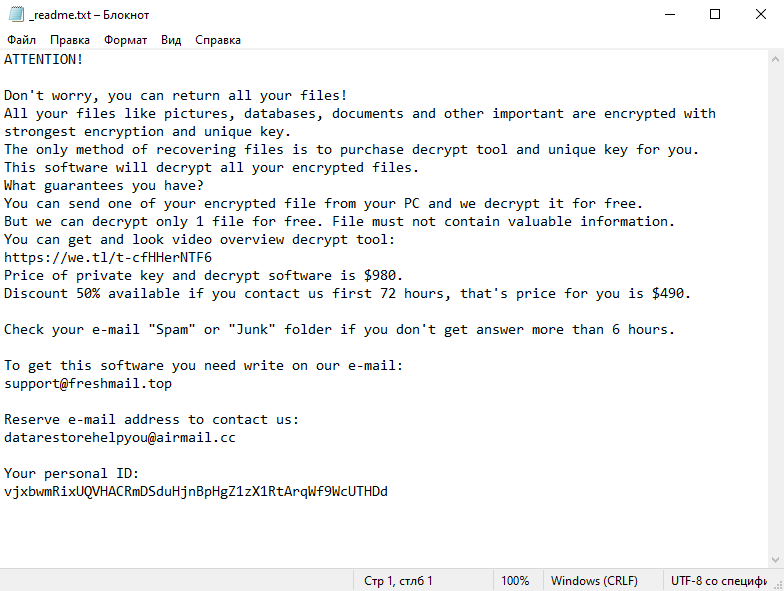
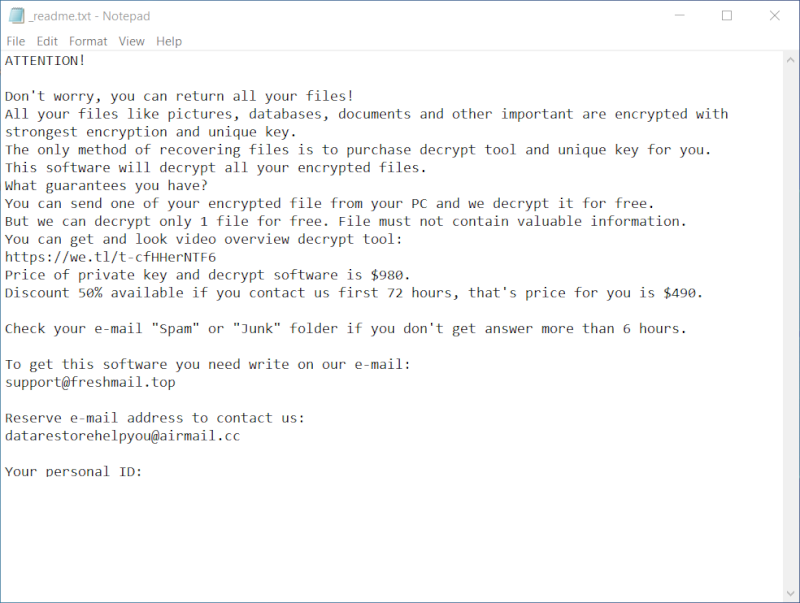
Ransom Note:
After the encryption process, Cdmx Ransomware generates a ransom note, typically named _readme.txt. The note contains information about the encryption and instructions on how to pay the ransom to get the decryption key. It’s usually placed in every folder that contains encrypted files.
Decryption Tools:
As of now, there are no specific decryption tools designed for Cdmx Ransomware. However, Emsisoft has developed a decryption tool for the STOP Djvu family, which Cdmx Ransomware is a part of. The tool may not always work, especially if the ransomware used an online key for the encryption, but it’s worth trying.
How to Decrypt Files:
To decrypt the encrypted files, you would need the decryption tool and the unique decryption key, which is typically held by the attackers. When using the Emsisoft STOP Djvu decryptor, you must download and run the tool, then follow the on-screen instructions. However, it’s important to remove the ransomware from your system first to prevent further encryption.
Keep in mind that paying the ransom is not recommended, as there is no guarantee the attackers will provide the decryption key. It’s always best to keep regular backups of your important files to prevent data loss from such attacks.
Read more